With the release of vSphere 7.0 Update 1, vSphere Cluster Services VMs (vCLS) appeared in vSphere clusters for the first time. This made cluster functions such as Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) and others independent of the availability of the vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA) for the first time. The latter still represents a single point of failure in the cluster. By outsourcing the DRS function to the redundant vCLS machines, a higher degree of resilience has been achieved.
Retreat Mode
The vSphere administrator has little influence on the provisioning of these VMs. Occasionally, however, it is necessary to remove these VMs from a datastore if it is to be put into maintenance mode, for example. There is a procedure for setting the cluster to retreat mode. This involves setting temporary advanced settings that lead to the deletion of the vCLS VMs by the cluster.
According to the VMware procedure, the Domain ID must be determined to activate Retreat Mode. The domain ID is the numerical value between ‘domain-c’ and the following colon. In the example from my lab, it has the value 8, but the number can also have four digits or more.

The domain ID has to be transferred to the Advanced Settings of the vCenter.
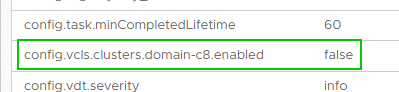
config.vcls.clusters.domain-c8.enabled = false
Admin error occured during activation of retreat mode.
After activating retreat mode on a vSAN cluster, administrators had lost all privileges to all objects in the vSphere Client.

A review of the services showed that the vCenter Server Daemon (vpxd) was not running.
Continue reading “Cluster Retreat Mode gone wrong – vSphere Client lockout”